MCI Codes
MCI Codes
ENiGMA½ supports a variety of MCI codes. Some predefined codes produce information about the current user, system, or other statistics while others are used to instantiate a View.
General Information
MCI codes are composed of two characters and are prefixed with a percent (%) symbol.
![]() To explicitly tie a MCI to a specific View ID, suffix the MCI code with a number. For example:
To explicitly tie a MCI to a specific View ID, suffix the MCI code with a number. For example: %BN1.
![]() Standard (non-focus) and focus colors are set by placing duplicate codes back to back in art files:
Standard (non-focus) and focus colors are set by placing duplicate codes back to back in art files:
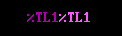
Some MCI codes have additional options that may be set directly from the code itself while others – and more advanced options – are controlled via the current theme.
Relationship with Menus, Art, and Themes
A MCI code that appears in a menu.hjson entry corresponds to that found in it’s associated art file. This same MCI code can be referenced in the theme.hjson in order to apply a theme.
See Menus and Themes for more information.
Predefined Codes
There are many predefined MCI codes that can be used anywhere on the system (placed in any art file).
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
BN |
Board Name |
VL |
Version label, e.g. “ENiGMA½ v0.0.12-beta” |
VN |
Version number, eg.. “0.0.12-beta” |
SN |
SysOp username |
SR |
SysOp real name |
SL |
SysOp location |
SA |
SysOp affiliations |
SS |
SysOp sex |
SE |
SysOp email address |
UN |
Current user’s username |
UI |
Current user’s user ID |
UG |
Current user’s group membership(s) |
UR |
Current user’s real name |
LO |
Current user’s location |
UA |
Current user’s age |
BD |
Current user’s birthday (using theme date format) |
US |
Current user’s sex |
UE |
Current user’s email address |
UW |
Current user’s web address |
UF |
Current user’s affiliations |
UT |
Current user’s theme name |
UD |
Current user’s theme ID (e.g. “luciano_blocktronics”) |
UC |
Current user’s login/call count |
ND |
Current user’s connected node number |
IP |
Current user’s IP address |
ST |
Current user’s connected server name (e.g. “Telnet” or “SSH”) |
FN |
Current user’s active file base filter name |
DN |
Current user’s number of downloads |
DK |
Current user’s download amount (formatted to appropriate bytes/megs/etc.) |
UP |
Current user’s number of uploads |
UK |
Current user’s upload amount (formatted to appropriate bytes/megs/etc.) |
NR |
Current user’s upload/download ratio |
KR |
Current user’s upload/download bytes ratio |
MS |
Current user’s account creation date (using theme date format) |
PS |
Current user’s post count |
PC |
Current user’s post/call ratio |
MD |
Current user’s status/viewing menu/activity |
MA |
Current user’s active message area name |
MC |
Current user’s active message conference name |
ML |
Current user’s active message area description |
CM |
Current user’s active message conference description |
SH |
Current user’s term height |
SW |
Current user’s term width |
AC |
Current user’s total achievements |
AP |
Current user’s total achievement points |
DR |
Current user’s number of door runs |
DM |
Current user’s total amount of time spent in doors |
DT |
Current date (using theme date format) |
CT |
Current time (using theme time format) |
OS |
System OS (Linux, Windows, etc.) |
OA |
System architecture (x86, x86_64, arm, etc.) |
SC |
System CPU model |
NV |
System underlying Node.js version |
AN |
Current active node count |
TC |
Total login/calls to the system ever |
TT |
Total login/calls to the system today |
RR |
Displays a random rumor |
SD |
Total downloads, system wide |
SO |
Total downloaded amount, system wide (formatted to appropriate bytes/megs/etc.) |
SU |
Total uploads, system wide |
SP |
Total uploaded amount, system wide (formatted to appropriate bytes/megs/etc.) |
TF |
Total number of files on the system |
TB |
Total amount of files on the system (formatted to appropriate bytes/megs/gigs/etc.) |
TP |
Total messages posted/imported to the system currently |
PT |
Total messages posted/imported to the system today |
Some additional special case codes also exist:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
CF## |
Moves the cursor position forward ## characters |
CB## |
Moves the cursor position back ## characters |
CU## |
Moves the cursor position up ## characters |
CD## |
Moves the cursor position down ## characters |
XY |
A special code that may be utilized for placement identification when creating menus or to extend an otherwise empty space in an art file down the screen. |
![]() More are added all
the time so also check out core/predefined_mci.js
for a full listing.
More are added all
the time so also check out core/predefined_mci.js
for a full listing.
![]() Many codes attempt to pay homage to Oblivion/2, iNiQUiTY, etc.
Many codes attempt to pay homage to Oblivion/2, iNiQUiTY, etc.
Views
A View is a control placed on a form that can display variable data or collect input. One example of a View is
a Vertical Menu (%VM): Old-school BBSers may recognize this as a lightbar menu.
| Code | Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
TL |
Text Label | Displays text | Static content. See Text View |
ET |
Edit Text | Collect user input | Single line entry. See Edit Text |
ME |
Masked Edit Text | Collect user input using a mask | See Masked Edit and Mask Edits below. |
MT |
Multi Line Text Edit | Multi line edit control | Used for FSE, display of FILE_ID.DIZ, etc. See Multiline Text Edit |
BT |
Button | A button | …it’s a button. See Button |
VM |
Vertical Menu | A vertical menu | AKA a vertical lightbar; Useful for lists. See Vertical Menu |
HM |
Horizontal Menu | A horizontal menu | AKA a horizontal lightbar. See Horizontal Menu |
FM |
Full Menu | A menu that can go both vertical and horizontal. | See Full Menu |
SM |
Spinner Menu | A spinner input control | Select one from multiple options. See Spinner Menu |
TM |
Toggle Menu | A toggle menu | Commonly used for Yes/No style input. See Toggle Menu |
PL |
Predefined Label | Show environment information | See Predefined Label |
KE |
Key Entry | A single key input control | Think hotkeys |
![]() Peek at /core/mci_view_factory.js to see additional information.
Peek at /core/mci_view_factory.js to see additional information.
Mask Edits
Mask Edits (%ME) use the special maskPattern property to control a mask. This can be useful for gathering dates, phone numbers, so on.
maskPattern’s can be composed of the following characters:
-
#: Numeric 0-9 -
A: Alpha a-z, A-Z -
@: Alphanumeric (combination of the previous patterns) -
&: Any “printable” character
Any other characters are literals.
An example of a mask for a date may look like this: ##/##/####.
Additionally, the following theme stylers can be applied:
-
styleSGR1: Controls literal character colors for non-focused controls -
styleSGR2: Controls literal character colors for focused controls -
styleSGR3: Controls fill colors (characters that have not yet received input).
All of the style properties can take pipe codes such as |00|08.
View Identifiers
As mentioned above, MCI codes can (and often should) be explicitly tied to a View Identifier. Simply speaking this is a number representing the particular view. These can be useful to reference in code, apply themes, etc.
A view ID is tied to a MCI code by specifying it after the code. For example: %VM1 or %SM10.
Properties & Theming
Predefined MCI codes and other Views can have properties set via menu.hjson and further themed via theme.hjson. See Themes for more information on this subject.
Common Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
textStyle |
Sets the standard (non-focus) text style. See Text Styles below |
focusTextStyle |
Sets focus text style. See Text Styles below. |
itemSpacing |
Used to separate items in menus such as Vertical Menu and Horizontal Menu Views. |
height |
Sets the height of views such as menus that may be > 1 character in height |
width |
Sets the width of a view |
focus |
If set to true, establishes initial focus |
text |
(initial) text of a view |
submit |
If set to true any accept action upon this view will submit the encompassing form
|
itemFormat |
Sets the format for a list entry. See Entry Formatting below |
focusItemFormat |
Sets the format for a focused list entry. See Entry Formatting below |
These are just a few of the properties set on various views. Use the source Luke, as well as taking a look at the default menu.hjson and theme.hjson files!
Custom Properties
Often a module will provide custom properties that receive format objects (See Entry Formatting below). Custom property formatting can be declared in the config block. For example, browseInfoFormat10…N (where N is up to 99) in the file_area_list module received a fairly extensive format object that contains {fileName}, {estReleaseYear}, etc.
Text Styles
Standard style types available for textStyle and focusTextStyle:
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
normal |
Leaves text as-is. This is the default. |
upper |
ENIGMA BULLETIN BOARD SOFTWARE |
lower |
enigma bulletin board software |
title |
Enigma Bulletin Board Software |
first lower |
eNIGMA bULLETIN bOARD sOFTWARE |
small vowels |
eNiGMa BuLLeTiN BoaRD SoFTWaRe |
big vowels |
EniGMa bUllEtIn bOArd sOftwArE |
small i |
ENiGMA BULLETiN BOARD SOFTWARE |
mixed |
EnIGma BUlLEtIn BoaRd SOfTWarE (randomly assigned) |
l33t |
3n1gm4 bull371n b04rd 50f7w4r3 |
Entry Formatting
Various strings can be formatted using a syntax that allows width & precision specifiers, text styling, etc. Depending on the context, various elements can be referenced by {name}. Additional text styles can be supplied as well. The syntax is largely modeled after Python’s string format mini language.
Additional Text Styles
Some of the text styles mentioned above are also available in the mini format language:
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
normal |
Leaves text as-is. This is the default. |
toUpperCase or styleUpper
|
ENIGMA BULLETIN BOARD SOFTWARE |
toLowerCase or styleLower
|
enigma bulletin board software |
styleTitle |
Enigma Bulletin Board Software |
styleFirstLower |
eNIGMA bULLETIN bOARD sOFTWARE |
styleSmallVowels |
eNiGMa BuLLeTiN BoaRD SoFTWaRe |
styleBigVowels |
EniGMa bUllEtIn bOArd sOftwArE |
styleSmallI |
ENiGMA BULLETiN BOARD SOFTWARE |
styleMixed |
EnIGma BUlLEtIn BoaRd SOfTWarE (randomly assigned) |
styleL33t |
3n1gm4 bull371n b04rd 50f7w4r3 |
Additional text styles are available for numbers:
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
sizeWithAbbr |
File size (converted from bytes) with abbreviation such as 1 MB, 2.2 GB, 34 KB, etc. |
sizeWithoutAbbr |
Just the file size (converted from bytes) without the abbreviation. For example: 1024 becomes 1. |
sizeAbbr |
Just the abbreviation given a file size (converted from bytes) such as MB or GB. |
countWithAbbr |
Count with abbreviation such as 100 K, 4.3 B, etc. |
countWithoutAbbr |
Just the count |
countAbbr |
Just the abbreviation such as M for millions. |
durationHours |
Converts the provided hours value to something friendly such as 4 hours, or 4 days. |
durationMinutes |
Converts the provided minutes to something friendly such as 10 minutes or 2 hours
|
durationSeconds |
Converts the provided seconds to something friendly such as 23 seconds or 2 minutes
|
Examples
Suppose a format object contains the following elements: userName and affils. We could create a itemFormat entry that builds a item to our specifications: |04{userName!styleFirstLower} |08- |13{affils}. This may produce a string such as this:

![]() Remember that a Python string format mini language style syntax is available for widths, alignment, number prevision, etc. as well. A number can be made to be more human readable for example:
Remember that a Python string format mini language style syntax is available for widths, alignment, number prevision, etc. as well. A number can be made to be more human readable for example: {byteSize:,} may yield “1,123,456”.
